MPC5534MVZ66R2 데이터 시트보기 (PDF) - Freescale Semiconductor
부품명
상세내역
제조사
MPC5534MVZ66R2 Datasheet PDF : 50 Pages
| |||
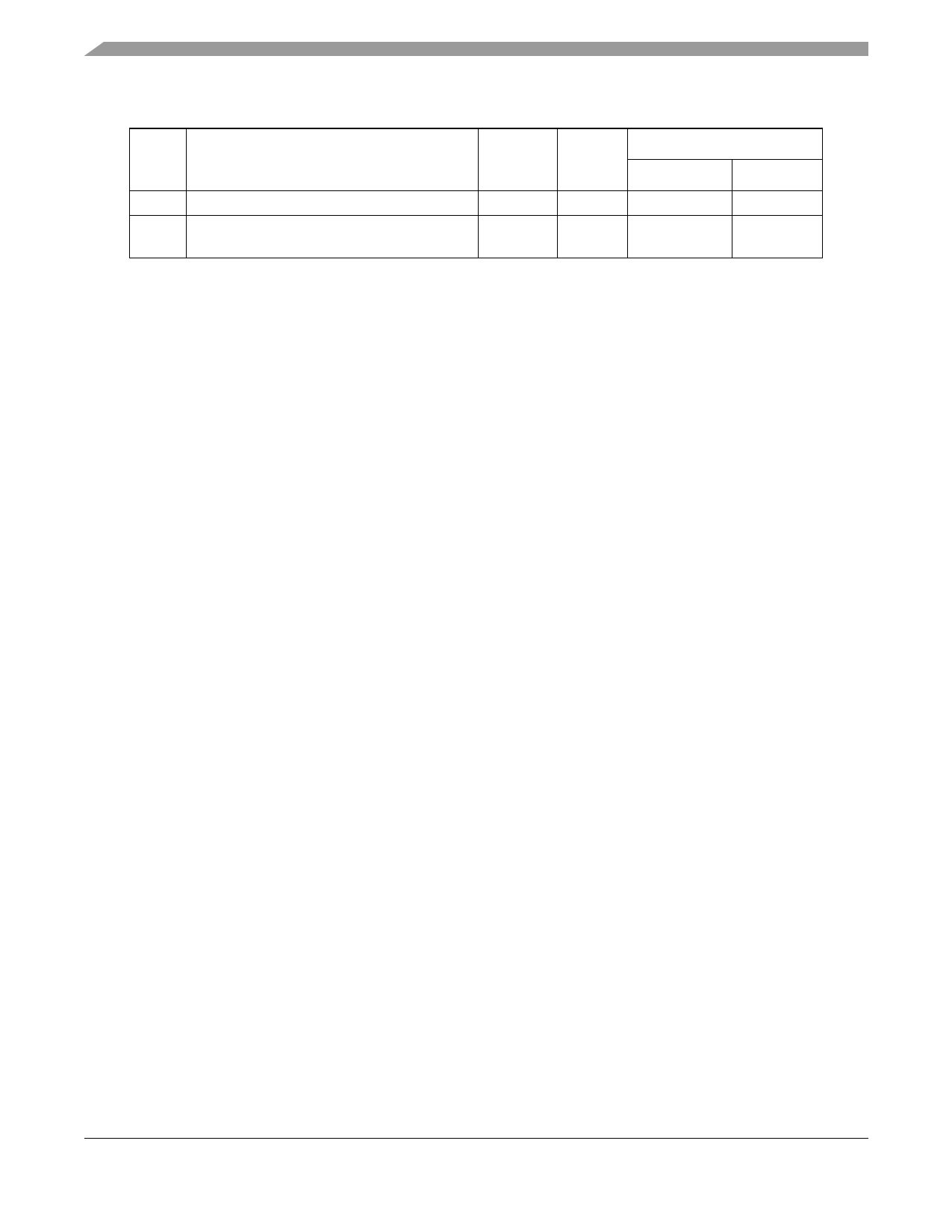
Electrical Characteristics
Table 3. Thermal Characteristics (continued)
Num
Characteristic
Symbol
Value
Unit
208 MAPBGA 324 PBGA
6 Junction to Case 5
7 Junction to Package Top 6
Natural Convection
RθJC
°C/W
8
10
ΨJT
°C/W
2
2
1 Junction temperature is a function of on-chip power dissipation, package thermal resistance, mounting site
(board) temperature, ambient temperature, air flow, power dissipation of other components on the board, and
board thermal resistance.
2 Per SEMI G38-87 and JEDEC JESD51-2 with the single layer board horizontal.
3 Per JEDEC JESD51-6 with the board horizontal.
4 Thermal resistance between the die and the printed circuit board per JEDEC JESD51-8. Board temperature is
measured on the top surface of the board near the package.
5 Indicates the average thermal resistance between the die and the case top surface as measured by the cold
plate method (MIL SPEC-883 Method 1012.1) with the cold plate temperature used for the case temperature.
6 Thermal characterization parameter indicating the temperature difference between package top and the
junction temperature per JEDEC JESD51-2.
3.2.1 General Notes for Specifications at Maximum Junction Temperature
An estimation of the chip junction temperature, TJ, can be obtained from the equation:
TJ = TA + (RθJA × PD)
where:
TA = ambient temperature for the package (oC)
RθJA = junction to ambient thermal resistance (oC/W)
PD = power dissipation in the package (W)
The supplied thermal resistances are provided based on JEDEC JESD51 series of standards to provide
consistent values for estimations and comparisons. The difference between the values determined on the
single-layer (1s) board and on the four-layer board with two signal layers and a power and a ground plane
(2s2p) clearly demonstrate that the effective thermal resistance of the component is not a constant. It
depends on the construction of the application board (number of planes), the effective size of the board
which cools the component, how well the component is thermally and electrically connected to the planes,
and the power being dissipated by adjacent components.
Connect all the ground and power balls to the respective planes with one via per ball. Using fewer vias to
connect the package to the planes reduces the thermal performance. Thinner planes also reduce the thermal
performance. When the clearance between through vias leave the planes virtually disconnected, the
thermal performance is also greatly reduced.
As a general rule, the value obtained on a single layer board is appropriate for the tightly packed printed
circuit board. The value obtained on the board with the internal planes is usually appropriate if the
application board has one oz (35 micron nominal thickness) internal planes, the components are well
separated, and the overall power dissipation on the board is less than 0.02 W/cm2.
MPC5534 Microcontroller Data Sheet, Rev. 0
6
Preliminary—Subject to Change Without Notice
Freescale Semiconductor