ACPL-M61T-000E 데이터 시트보기 (PDF) - Avago Technologies
부품명
상세내역
제조사
ACPL-M61T-000E
ACPL-M61T-000E Datasheet PDF : 10 Pages
| |||
Propagation Delay, Pulse-Width Distortion and Propa-
gation Delay Skew
Propagation delay is a figure of merit which describes
how quickly a logic signal propagates through a system.
The propagation delay from low to high (tPLH) is the
amount of time required for an input signal to propagate
to the output, causing the output to change from low
to high. Similarly, the propagation delay from high to
low (tPHL) is the amount of time required for the input
signal to propagate to the output, causing the output to
change from high to low (see Figure 6).
Pulse-width distortion (PWD) results when tPLH and tPHL
differ in value. PWD is defined as the difference between
tPLH and tPHL and often determines the maximum data
rate capability of a transmission system. PWD can be
expressed in percent by dividing the PWD (in ns) by
the minimum pulse width (in ns) being transmitted.
Typically, PWD on the order of 20-30% of the minimum
pulse width is tolerable; the exact figure depends on the
particular application (RS232, RS422, T-1, etc.).
Propagation delay skew, tPSK, is an important parameter
to consider in parallel data applications where synchro-
nization of signals on parallel data lines is a concern.
If the parallel data is being sent through a group of op-
tocouplers, differences in propagation delays will cause
the data to arrive at the outputs of the optocouplers at
different times. If this difference in propagation delays
is large enough, it will determine the maximum rate at
which parallel data can be sent through the optocou-
plers.
Propagation delay skew is defined as the difference
between the minimum and maximum propagation
delays, either tPLH or tPHL, for any given group of opto-
couplers which are operating under the same conditions
(i.e., the same drive current, supply voltage, output load,
and operating temperature). As illustrated in Figure 14,
if the inputs of a group of optocouplers are switched
either ON or OFF at the same time, tPSK is the difference
between the shortest propagation delay, either tPLH or
tPHL, and the longest propagation delay, either tPLH or
tPHL.
As mentioned earlier, tPSK can determine the maximum
parallel data transmission rate. Figure 15 is the timing
diagram of a typical parallel data application with both
the clock and the data lines being sent through opto-
couplers. The figure shows data and clock signals at the
inputs and outputs of the optocouplers. To obtain the
maximum data transmission rate, both edges of the clock
signal are being used to clock the data; if only one edge
were used, the clock signal would need to be twice as
fast.
Propagation delay skew represents the uncertainty of
where an edge might be after being sent through an op-
tocoupler. Figure 15 shows that there will be uncertainty
in both the data and the clock lines. It is important that
these two areas of uncertainty not overlap, otherwise the
clock signal might arrive before all of the data outputs
have settled, or some of the data outputs may start to
change before the clock signal has arrived. From these
considerations, the absolute minimum pulse width that
can be sent through optocouplers in a parallel applica-
tion is twice tPSK. A cautious design should use a slightly
longer pulse width to ensure that any additional uncer-
tainty in the rest of the circuit does not cause a problem.
The tPSK specified optocouplers offer the advantages
of guaranteed specifications for propagation delays,
pulse-width distortion and propagation delay skew over
the recommended temperature, and input current, and
power supply ranges.
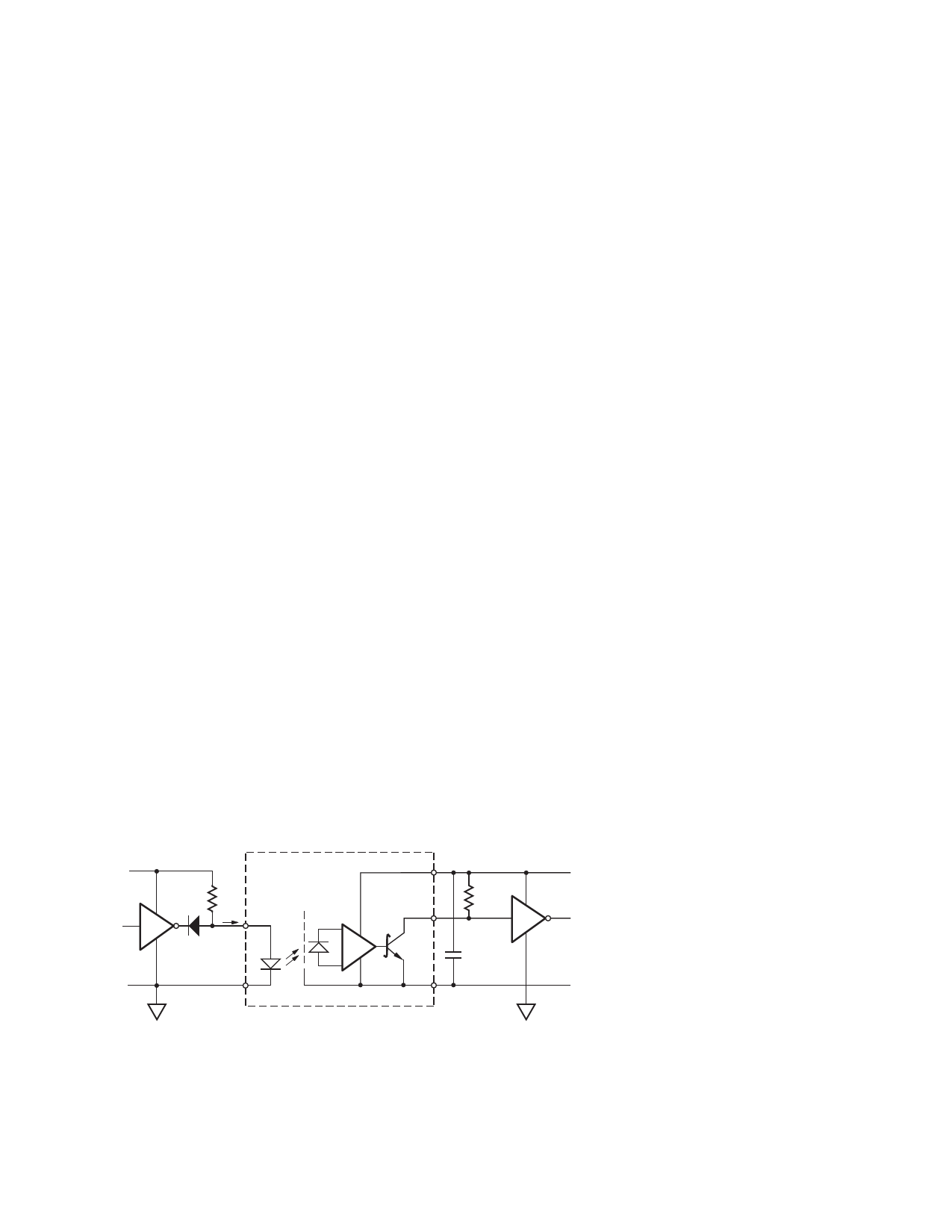
VCC 1 5 V
GND 1
470
IF 1
*D1
VF
3
1
SHIELD
* DIODE D1 (1N916 OR EQUIVALENT) IS NOT REQUIRED
FOR UNITS WITH OPEN COLLECTOR OUTPUT.
Figure 13. Recommended TTL/LSTTL to TTL/LSTTL Interface Circuit.
6
390 Ω
5
0.1 μF
BYPASS
4
5V
2
V CC 2
GND 2
9