ADD5207 데이터 시트보기 (PDF) - Analog Devices
부품명
상세내역
제조사
ADD5207 Datasheet PDF : 16 Pages
| |||
Data Sheet
ADD5207
THEORY OF OPERATION
CURRENT MODE, STEP-UP SWITCHING
REGULATOR OPERATION
The ADD5207 uses a current mode PWM boost regulator to
generate the minimum voltage needed to drive the LED string
at the programmed LED current. The current mode regulation
system allows a fast transient response while maintaining a
stable output voltage. By selecting the proper resistor-capacitor
network from COMP to GND, the regulator response is
optimized for a wide range of input voltages, output voltages,
and load conditions. The ADD5207 can provide a 36 V maxi-
mum output voltage and drive up to 10 LEDs (3.4 V/25 mA
type of LEDs) for each channel.
INTERNAL 3.3 V REGULATOR
The ADD5207 contains a 3.3 V linear regulator that
is used for biasing internal circuitry. The internal regulator
requires a 1 μF bypass capacitor. Place this bypass capacitor
between Pin VDD (Pin 8) and GND, as close as possible to
Pin VDD.
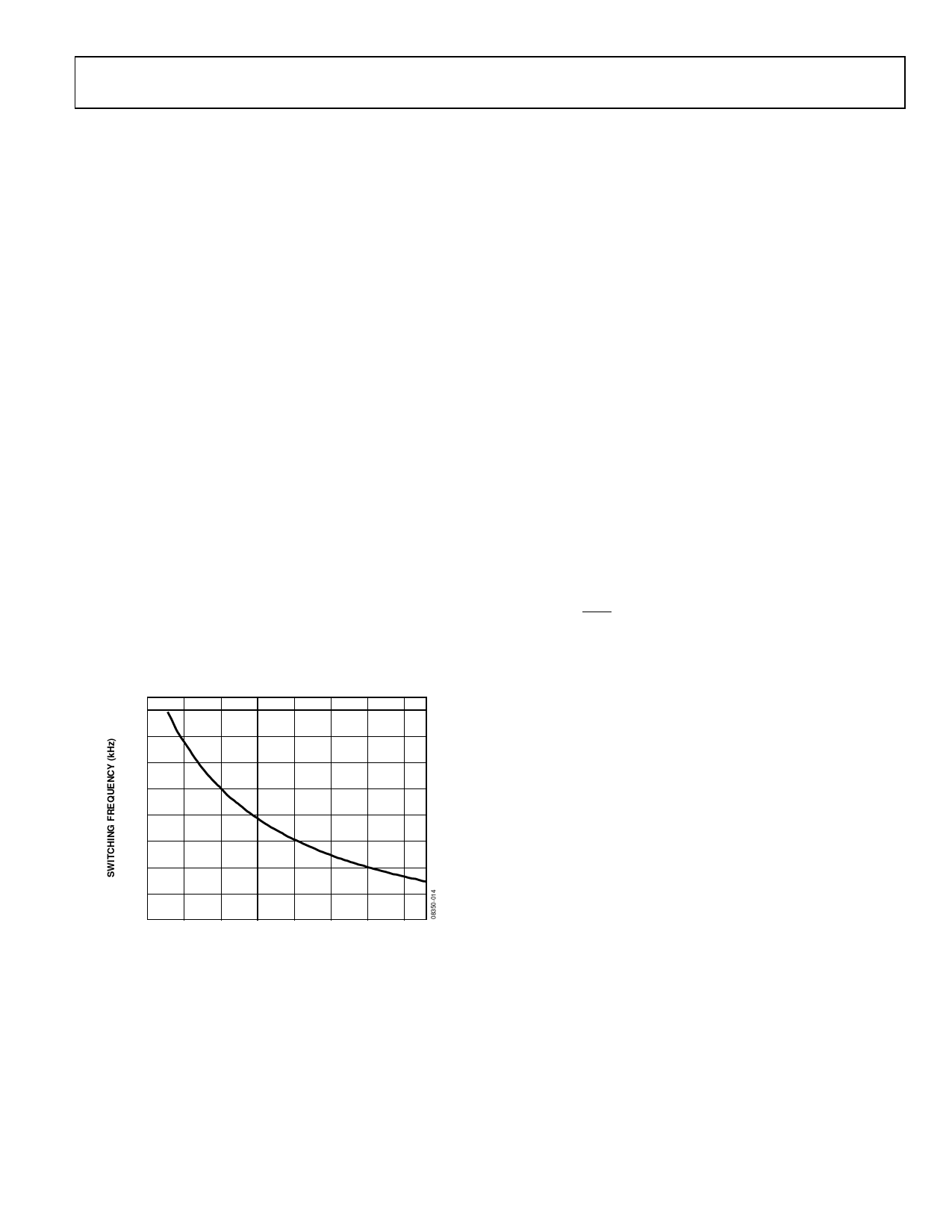
BOOST CONVERTER SWITCHING FREQUENCY
The ADD5207 boost converter switching frequency is user
adjustable, between 600 kHz to 1 MHz, by using an external
resistor, RF. A frequency of 600 kHz is recommended to optim-
ize the regulator for high efficiency, and a frequency of 1 MHz
is recommended to minimize the size of external components.
See Figure 14 for considerations when selecting a switching
frequency and an adjustment resistor (RF).
1000
900
800
700
600
500
400
300
80
100 120 140 160 180 200 220
RF (kΩ)
Figure 14. Switching Frequency vs. RF
DIMMING FREQUENCY (fPWM)
The ADD5207 contains an internal oscillator to generate the
PWM dimming signal for LED brightness control. The LED
dimming frequency (fPWM) is fixed at 8 kHz internally.
CURRENT SOURCE
The ADD5207 contains four current sources to provide accu-
rate current sinking for each LED string. String-to-string
tolerance is kept within ±1.5% at 20 mA. Each LED string
current is adjusted up to 25 mA using an external resistor.
The ADD5207 contains an LED open fault protection circuit
for each channel. If the headroom voltage of the current source
remains below 150 mV while the boost converter output reaches
the OVP level, the ADD5207 recognizes that the current source
has an open-load fault for the current source, and the current
source is disabled.
If an application requires three LED strings, each LED string
should be connected using FB1 to FB3. The unused FB4 pin
should be tied to GND.
The ADD5207 contains hysteresis to prevent the LED current
change that is caused by a ±0.195% jitter of the PWM input.
Programming the LED Current
As shown in the Figure 2, the ADD5207 has an LED current set
pin (ISET). A resistor (RSET) from this pin to ground adjusts the
LED current up to 25 mA. LED current level can be set with
following equation:
ILED = 3600 (A)
RSET
PWM DIMMING MODE
The ADD5207 supports 8-bit resolution to control brightness.
However, each current source has a minimum on time require-
ment for LED current regulation such that the dimming is in
the range of 1.5% to 100%. Accordingly, even when the PWM
input duty cycle is more than 0% and less than 1.5%, the LED
duty cycle is held at 1.5%.
Phase Shift PWM Dimming
There is a phase delay between each current source channel that is
programmed by the number of current sources in operation. If the
application requires four separate LED strings, each string has a
90 degree phase delay between channels. If three LED strings are
connected at the FB1 to FB3 pins (FB4 = GND), each string has a
120 degree phase delay.
SAFETY FEATURES
The ADD5207 contains several safety features to provide stable
and reliable operation.
Soft Start
The ADD5207 contains an internal soft start function to reduce
inrush current at startup. The soft start time is typically 1.1 ms.
Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
The ADD5207 contains OVP circuits to prevent boost converter
damage if the output voltage becomes excessive for any reason.
To keep a safe output level, the integrated OVP circuit monitors
Rev. A | Page 11 of 16