MLX90129 데이터 시트보기 (PDF) - Melexis Microelectronic Systems
부품명
상세내역
제조사
MLX90129 Datasheet PDF : 60 Pages
| |||
MLX90129
13.56MHZ SENSOR TAG / DATALOGGER IC
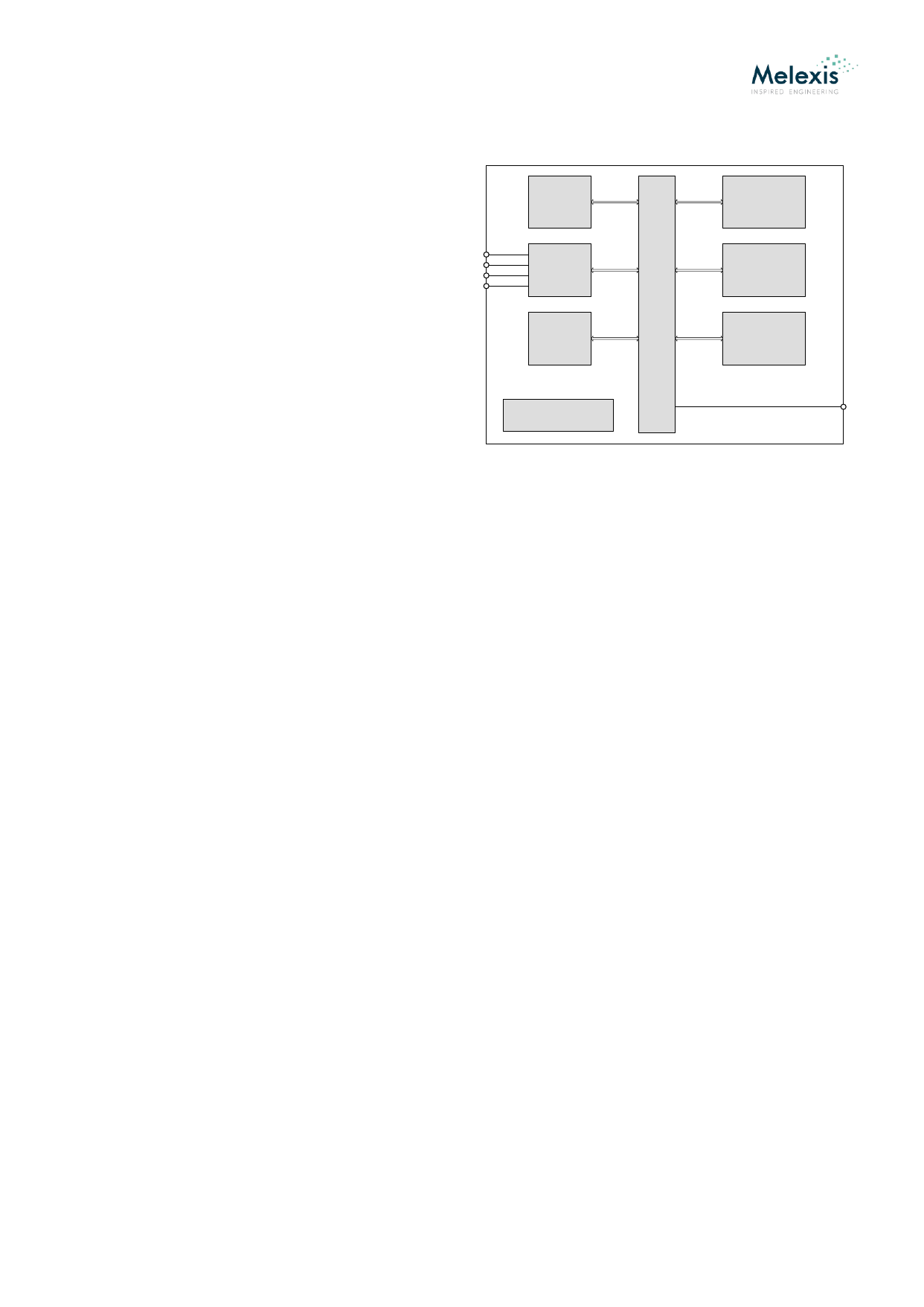
7.2. Digital Controller and memory domains
7.2.1. Digital controller
The main features of the digital part of MLX90129, called
Digital Controller are:
DMA
Direct
Memory
Access
Register File
Slave / Master SPI interface
RFID interface
DMA: Direct Memory Access
Register File controller
EEPROM controller
Sensor interface controller
Clock and Power management
Core: transactions arbiter and interrupt
manager
SS
SCLK
MISO
MOSI
SPI
RFID
interface
ISO15693
CORE
Clock and Power
manager
Eeprom &
EeLatches
interface
Sensor & ADC
Controller
IRQ
The digital controller manages the transactions between
the communication interfaces, the memories and the
sensor. It allows also a standalone mode with its DMA
unit. All these blocks are described in the next chapters.
The SPI and RFID communication ways can be used concurrently. The Core transaction arbiter handles the priorities and the
interrupts. It updates some status bits that may be used by the external microcontroller or the RFID base-station to optimize the
communication.
The Digital Controller of the MLX90129 allows the user to do the following tasks, via SPI or RFID:
_ Configure the sensor interface and the communication media.
_ Manage the power consumption, the interrupts, the security items,…
_ Run A/D conversions of the selected sensors.
_ Store (or read) data in the internal or in an external EEPROM.
_ Configure and start a standalone process (sleep – sense – interrupt or store – sleep - …)
_ Get the status of the current process.
All these tasks may be done by simply reading or writing the different memories: EEPROM, registers, ee-Latches, internal devices.
Thus, several address domains are defined to access them in an easy way.
7.2.2. Address domains
Four address domains have been defined to designate the memory and the non-memory devices that act during the requested
transactions:
- EEPROM address domain:
This domain addresses the non-volatile EEPROM. It is used to store the user-defined data and the image of the Register File that
can be automatically downloaded after a power-on. This memory block is energy independent and can store data even when the
MLX90129 is unpowered.
- Register File address domain:
This memory domain is used to store the current configuration information of all internal MLX90129 devices (Sensor interface,
Power management …). This memory is energy-dependent and must be updated each time the MLX90129 is turned-on.
- Internal Devices address domain:
This domain allows accessing the registers linked to the so-called internal devices like the ADC buffers, the status words of the
Core Transaction Arbiter and the EE-Latches. They may be accessed with the appropriate SPI / RFID commands including its
address. The difference with the Register File is the fact that they are not copied from the EEPROM at the start-up and they may
be used during the requested transaction.
REVISION 011 - JUNE 13, 2017
3901090129
Page 13 of 60