TC7106(2002) 데이터 시트보기 (PDF) - Microchip Technology
부품명
상세내역
제조사
TC7106 Datasheet PDF : 26 Pages
| |||
TC7106/A/TC7107/A
3.0 DETAILED DESCRIPTION
(All Pin designations refer to 40-Pin PDIP.)
3.1 Dual Slope Conversion Principles
The TC7106A and TC7107A are dual slope, integrating
analog-to-digital converters. An understanding of the
dual slope conversion technique will aid in following the
detailed operation theory.
The conventional dual slope converter measurement
cycle has two distinct phases:
• Input Signal Integration
• Reference Voltage Integration (De-integration)
The input signal being converted is integrated for a
fixed time period (TSI). Time is measured by counting
clock pulses. An opposite polarity constant reference
voltage is then integrated until the integrator output
voltage returns to zero. The reference integration time
is directly proportional to the input signal (TRI). See
Figure 3-1.
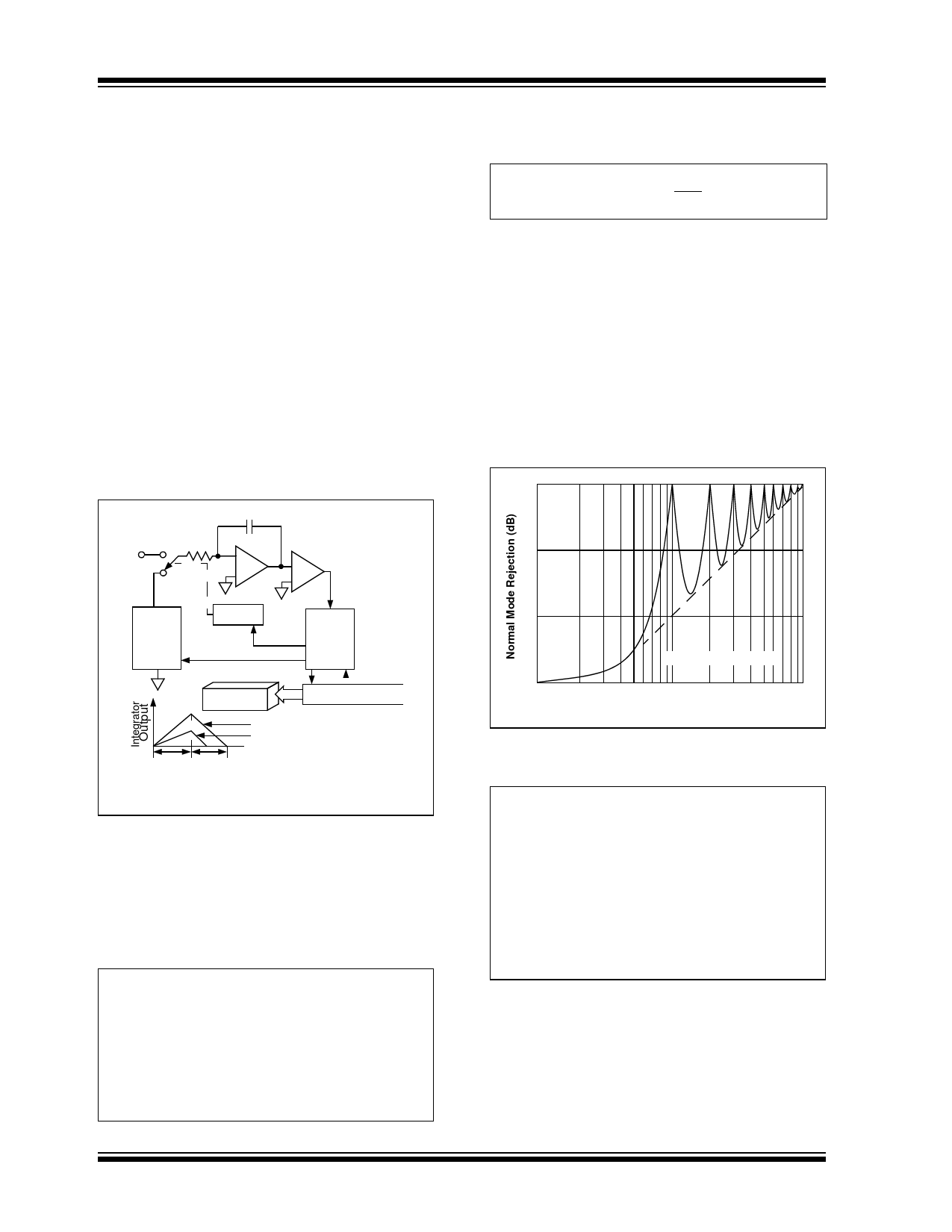
FIGURE 3-1:
Analog
Input
Signal
BASIC DUAL SLOPE
CONVERTER
C
Integrator
–
+
Comparator
–
+
+/–
REF
Voltage
Switch
Driver
Phase
Control
Polarity Control
Control
Logic
Clock
DISPLAY
VIN ≈ VREF
VIN ≈ 1/2 VREF
Counter
Fixed
Signal
Integrate
Time
Variable
Reference
Integrate
Time
In a simple dual slope converter, a complete conver-
sion requires the integrator output to “ramp-up” and
“ramp-down.” A simple mathematical equation relates
the input signal, reference voltage and integration time.
EQUATION 3-1:
1 TSI
RC ∫ 0 VIN(t)dt =
VRTRI
RC
Where:
VR = Reference voltage
TSI = Signal integration time (fixed)
TRI = Reference voltage integration time (variable).
For a constant VIN:
EQUATION 3-2:
VIN = VR
TRI
TSI
The dual slope converter accuracy is unrelated to the
integrating resistor and capacitor values as long as
they are stable during a measurement cycle. An inher-
ent benefit is noise immunity. Noise spikes are inte-
grated or averaged to zero during the integration
periods. Integrating ADCs are immune to the large con-
version errors that plague successive approximation
converters in high noise environments. Interfering sig-
nals with frequency components at multiples of the
averaging period will be attenuated. Integrating ADCs
commonly operate with the signal integration period set
to a multiple of the 50/60Hz power line period (see
Figure 3-2).
FIGURE 3-2:
30
NORMAL MODE
REJECTION OF DUAL
SLOPE CONVERTER
20
10
0
0.1/T
T = Measured Period
1/T
Input Frequency
10/T
DS21455B-page 8
© 2002 Microchip Technology Inc.